Can ChatGPT Be Our Creative Partner?: Evidence from PISA 2022
JUN 2023 - DEC 2024
Investigating distinct interaction patterns between young learners and GenAI in creative problem solving tasks.
Resources
Role
Skills
Project Overview
This project was conducted as part of Chohui Lee's master's thesis research. The study investigates how young learners collaborate with Generative AI (ChatGPT) to solve creative problems from the PISA 2022 Creative Thinking Assessment. By analyzing students' prompts across social and scientific domains and comparing high- and low-performing groups, the research reveals distinct patterns of learner–AI interaction and how learners engage with GenAI as a cognitive partner in creative problem solving.
*This work is currently published in ET&S (Q1, SSCI).
Problem We Found
“How do learners engage in the creative problem solving process with GenAI?”
As novel and complex problems continue to emerge, creative problem solving (CPS) has become a core competency for learners in today's VUCA world. It involves the ability to come up with solutions that are both original and useful.
The rapid rise of generative AI (GenAI) has opened up new possibilities for human–AI collaboration, offering support for learners' divergent and convergent thinking processes.
However, there's still limited understanding of how learners actually collaborate with GenAI in creative problem solving, and how we can design learning experiences that foster more effective human–AI collaboration.
Our Approach
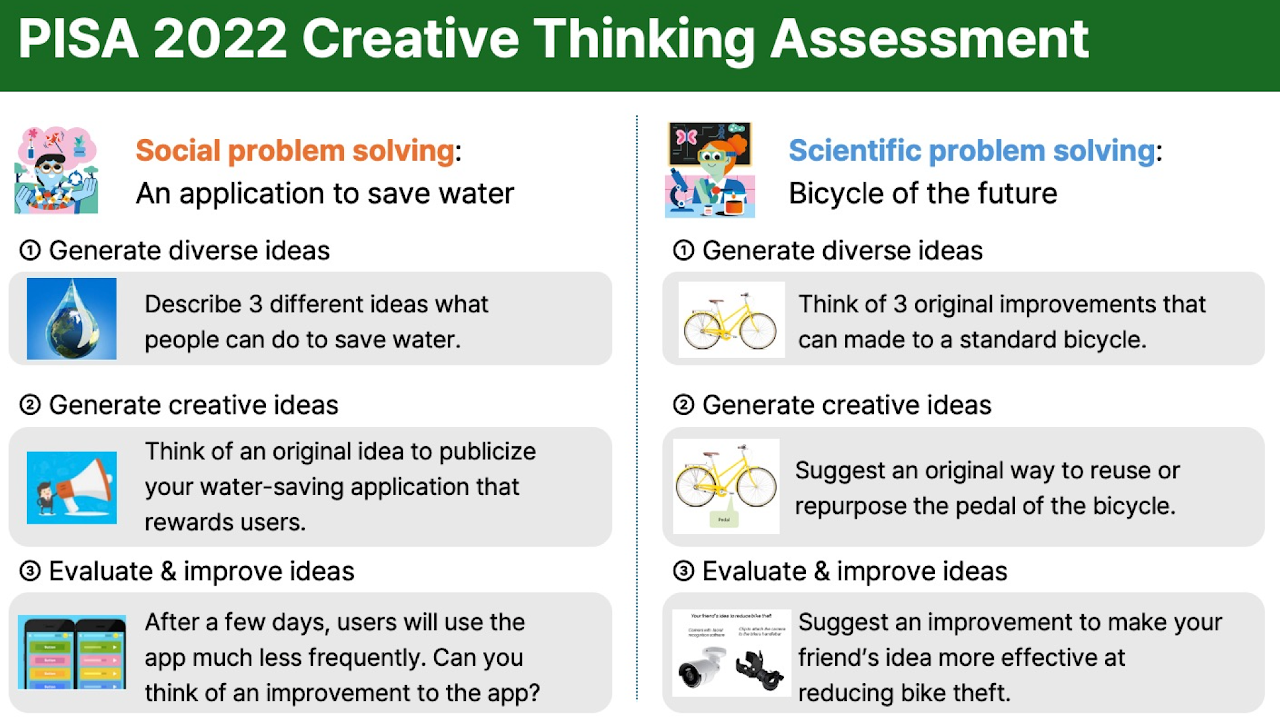
This study adopted creative problem-solving tasks from the PISA 2022 Creative Thinking Assessment, which takes a domain-specific approach to creativity across two problem areas: social and scientific. A total of 38 students aged 15 participated in the study.
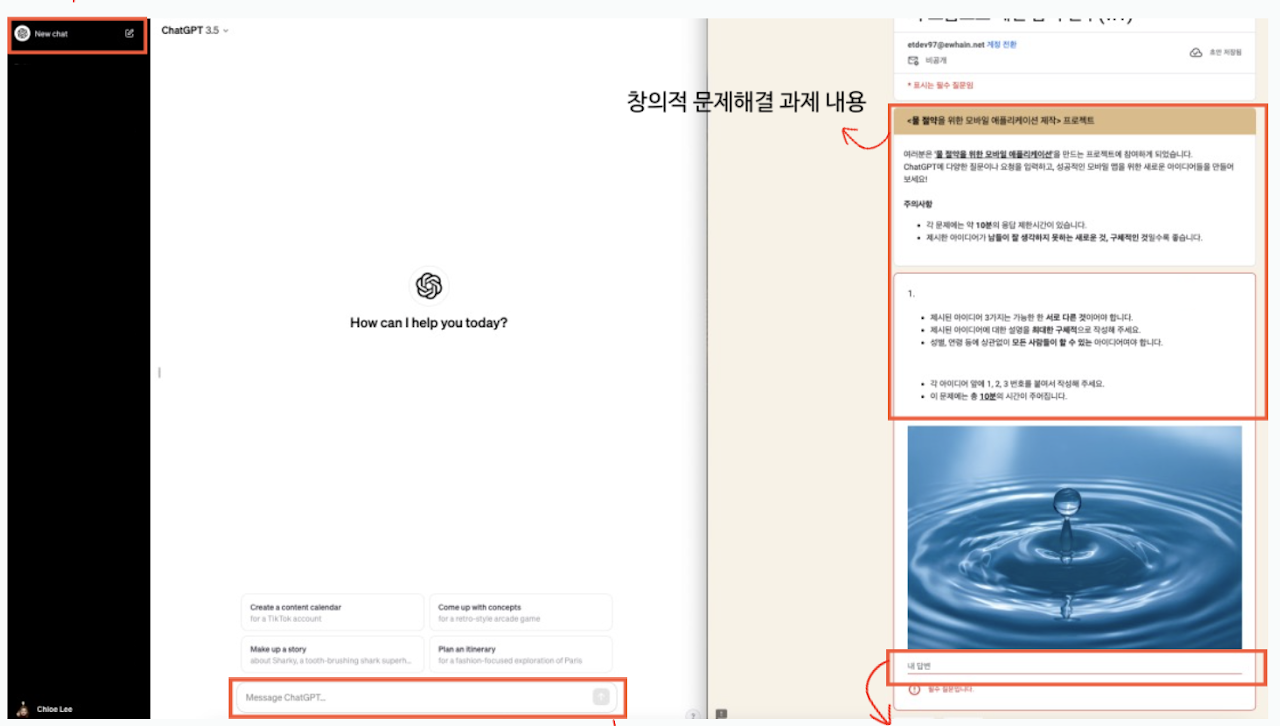
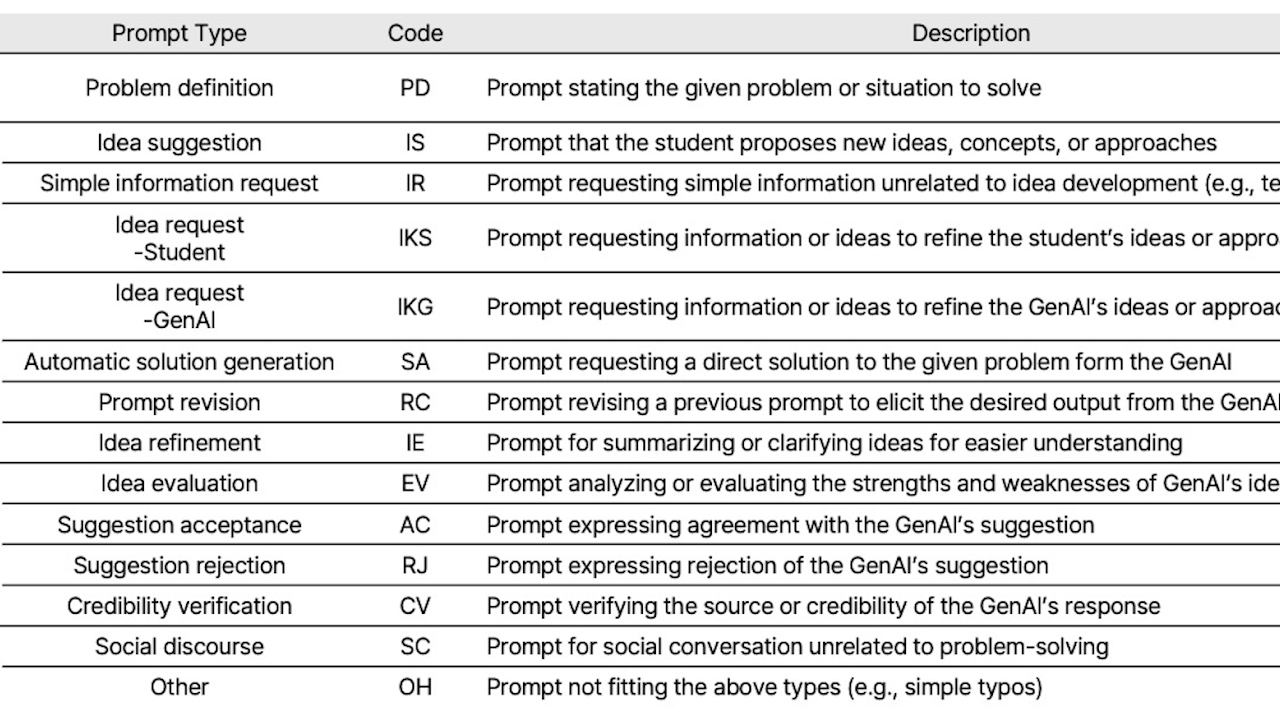
To examine how learners interacted with ChatGPT during the creative problem-solving process, the study collected and analyzed their prompt data and final solutions.
Key Results
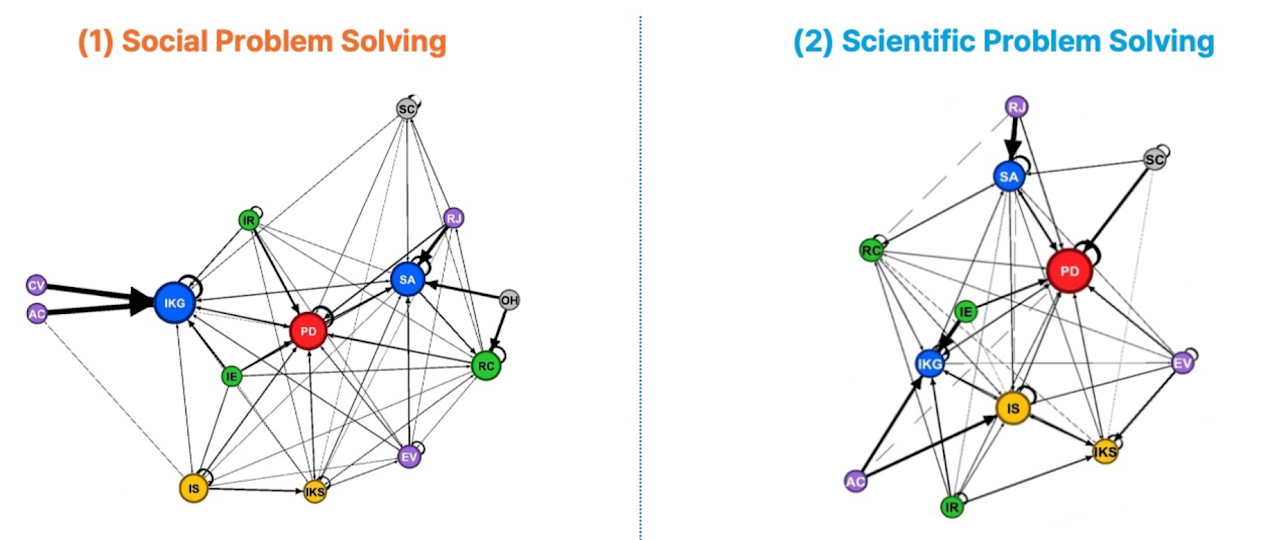
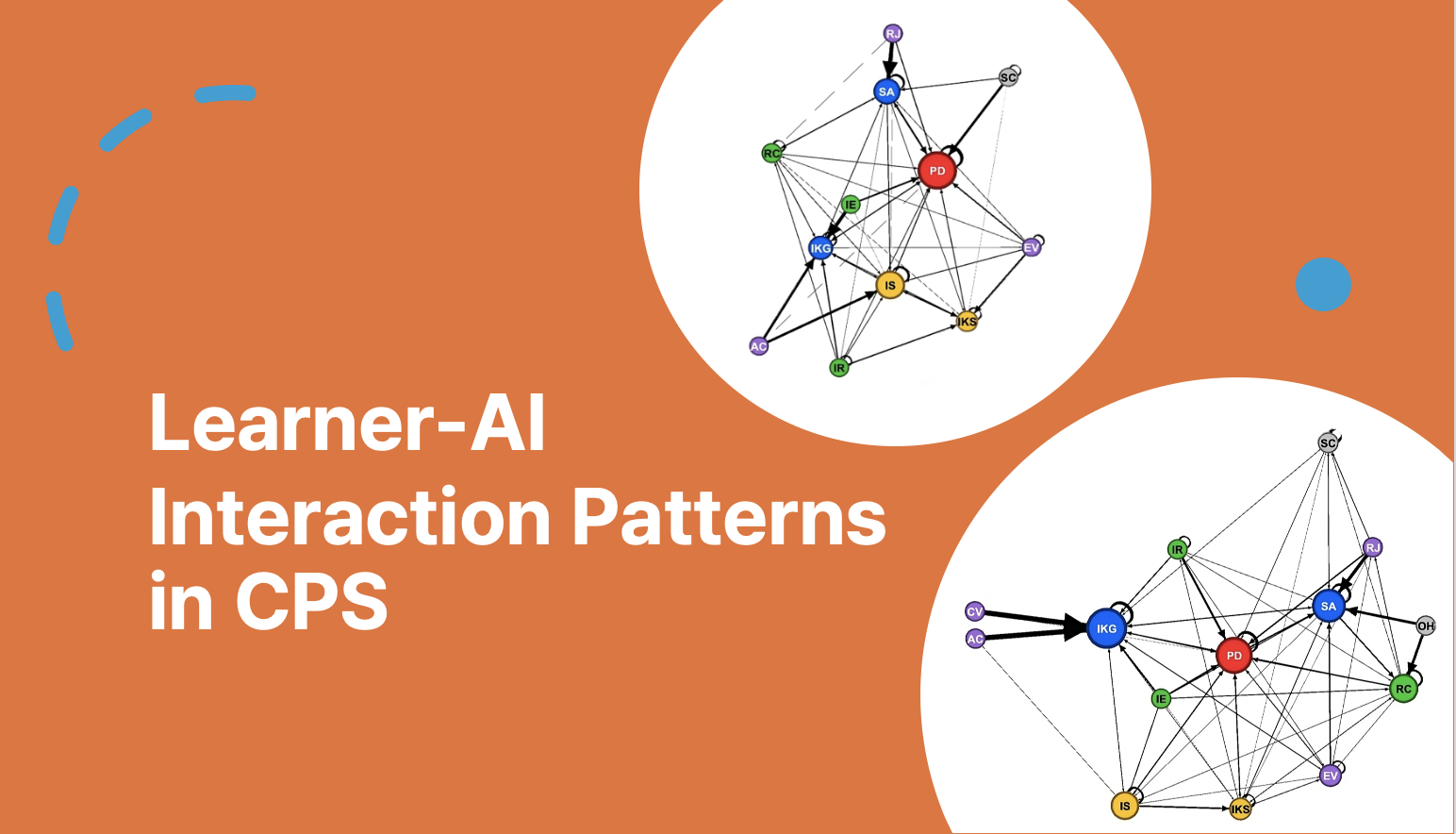
Learner-GenAI Interaction Patterns
- •Learner-GenAI Interaction Patterns through Prompts
- •Network analysis
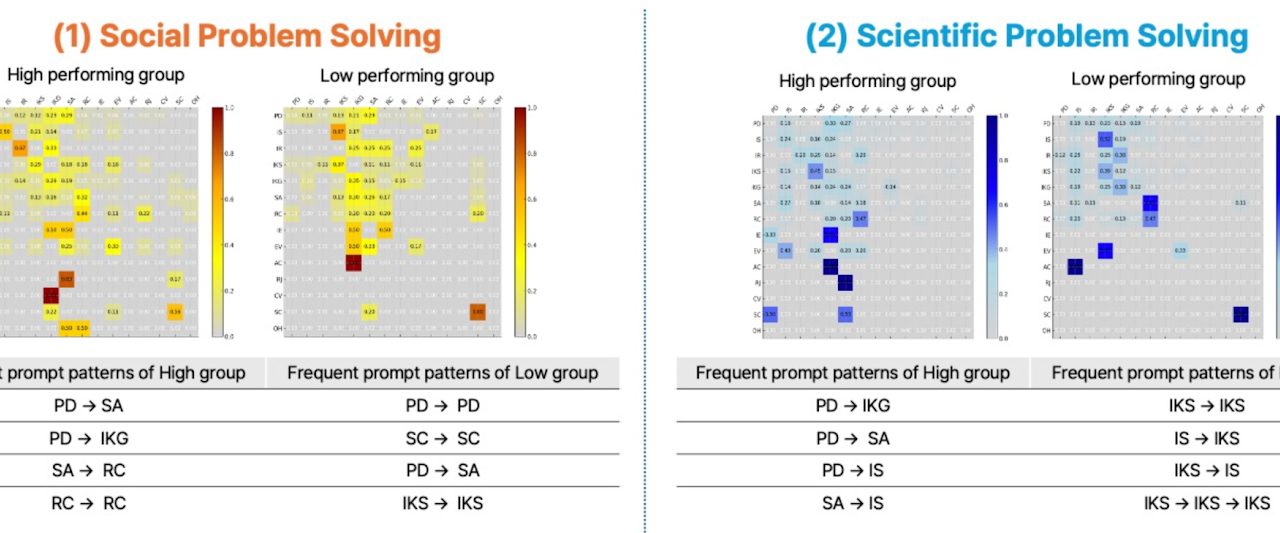
Differences in High and Low-performing Groups
- •Transition probability of prompt types used
- •Sequential pattern analysis
Domain-Specific Differences in Learner–AI Interaction
- •In social problems, students relied more on ChatGPT for direct answers or built their solutions around ChatGPT suggestions.
- •In scientific problems, they contributed more original ideas and maintained a better balance between their own reasoning and the model's input.
Differences in Learner-AI Collaboration by Performance Level
- •High-performing students used more diverse prompts and actively alternated between their own ideas and ChatGPT's, integrating both perspectives in the creative process.
- •In contrast, low-performing students relied on narrower prompt types and tended to focus on either their own ideas or the model's responses, showing limited collaboration between the two.
Recognition & Awards
- •Accepted to Educational Technology & Society, 28(4). [SSCI-indexed, Q1]
- •Received Outstanding Paper Award in 2024 Korean Society for Educational Technology & Korean Association for Educational Information and Media Joint Conference.